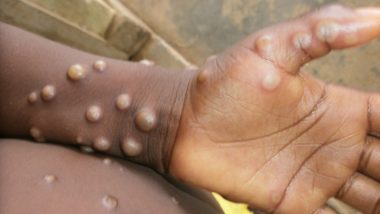
Mumbai, April 17: Is the world on the brink of another global health crisis? Could a new strain of monkeypox pose a pandemic threat? Recent research suggests so, as scientists have identified a concerning variant, termed "clade 1b," in a mining town in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) with "pandemic potential". With its enhanced ability to spread, this strain has raised alarm bells among global health experts, calling for urgent action to prevent a potential outbreak.
As per a report by the Telegraph, the discovery came amid the DRC's struggle to contain the spread of a deadlier form of the virus, known as "clade 1," which has already claimed hundreds of lives in the country, with mortality rates reaching 10 per cent among those infected. As per the report, last year alone, the country witnessed over 3,500 cases and 264 fatalities attributed to monkeypox. However, the emergence of clade 1b introduces a new dimension to the crisis, raising concerns about its potential to escalate nationally and internationally. Deadly Monkeypox Virus Identified in People With Advanced HIV Induced Weak Immunity: Study.
What is Clade 1b Mutation?
The Clade 1b mutated strain, identified in Kamituga, a densely populated mining town near the Rwandan border, is particularly worrisome due to its increased transmissibility, primarily through sexual contact. This mode of transmission is unusual for monkeypox, hinting at significant shifts in the virus's epidemiology. Scientists emphasise the urgent need for intervention to prevent the localised outbreak from spiralling into a national or even international crisis. The findings underscore the importance of swift action by both endemic countries and the global community to mitigate the risk of another global monkeypox epidemic.
Mpox, previously known for its global epidemic in 2022 primarily affecting gay and bisexual men, has taken a deadlier form in the DRC, known as "clade 1". This strain, responsible for significant mortality rates, has posed a persistent challenge for health authorities in the region. Despite efforts, the DRC has witnessed a surge in cases and fatalities, particularly among children, signalling the gravity of the situation. Mpox: Wastewater Detections Show Monkeypox Virus Likely Underestimated, More Virus DNA Present Than Expected.
The study, although not yet peer-reviewed, emphasizes the need for swift action from the international community to prevent another global outbreak of mpox. With the DRC already struggling to control the deadly "clade 1" variant, which has claimed numerous lives, the emergence of clade 1b poses a significant threat. The outbreak in Kamituga not only marks the first appearance of the virus in the region but also presents a shift in its transmission patterns.
Unlike previous outbreaks primarily affecting specific demographics, such as children, this instance predominantly targets adults, notably sex workers, raising questions about the evolving epidemiology of the disease. Addressing the Kamituga outbreak necessitates comprehensive measures, including surveillance, contact tracing, and targeted vaccinations. However, the region's healthcare infrastructure is ill-equipped to handle a large-scale epidemic, amplifying the urgency for immediate action to prevent further spread.
(The above story first appeared on LatestLY on Apr 17, 2024 01:04 PM IST. For more news and updates on politics, world, sports, entertainment and lifestyle, log on to our website latestly.com).












 Quickly
Quickly