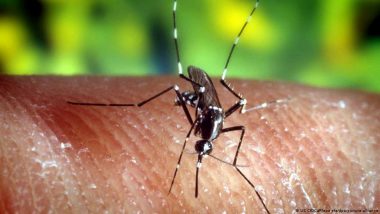
2023 saw the highest number of local, rather than imported, cases of dengue on the European mainland in nearly 80 years.Travel-related cases of dengue, like travel-related cases of malaria, are not uncommon in Europe. People get home from a trip to a hotspot, they come down with dengue, rest for a few days and then get back to their normal lives.
Problems arise when dengue-infected individuals find themselves in a statistically unlikely situation: the weather in their home country is warm, they live in an urban area, or they get bitten — at home — by an Aedes mosquito, which then carries the dengue virus to another person.
The chance of all these circumstances coming together in Europe is very low.
Cases of locally transmitted dengue on the European mainland are rare, as statistics collected between 2015 and 2019 show: European countries, where the mosquito that spreads dengue is established, saw about 3,000 cases of travel-related dengue, but only 9 cases of local transmitted dengue.
But in 2022, cases rose higher than in the past seven decades on the European mainland combined — with 65 cases in France alone.
In 2023, the number of cases rose even higher — over 110 cases, largely in France and Italy, and a handful in Spain.
How dengue spreads
Dengue is generally transmitted through the Aedes mosquito.
In order for local transmission to occur in Europe, the mosquito needs to have established itself in the community. That means, it needs to be able to live, breed and survive there. There are different types of aedes mosquito, but the one most widespread in Europe is the aedes albopictus.
Temperatures need to be high — between 15 and 35 degrees Celsius — for the mosquitos to thrive, so the threat is restricted to warmer months.
And the virus has to be introduced into the community. Because dengue is not endemic in Europe, this occurs when a traveler brings the virus from abroad.
Dengue is a viral infection that can involve high fever, headache and nausea, but the majority of cases are asymptomatic. Death is extremely rare but can occur in situations in which severe illness — also rare — goes untreated.
Why are numbers so high?
Experts say there are a lot of potential explanations for 2023's rise in locally transmitted dengue cases, but they say there's no clear answer yet.
"I believe that what we saw in southern France this past summer [2023] and in other parts of Southern Europe is part of a threshold phenomenon," Thomas Jaenisch, a professor of global health at the Colorado School of Public Health, told DW. "It is true that temperatures have been rising for a long time, but we have more and more [other] factors acting together synergistically."
Research conducted by Jaenisch helped provide evidence for the WHO's dengue classification of 2009, which distinguishes between severe and non-severe dengue.
Jaenisch said that weather, growing mosquito populations, increased occurrence of the virus abroad and vector control all offer some potential explanation of the trend observed over the past two years. We'll explain each of these threats below.
Higher temperatures
Higher temperatures, not only during the day but also at night, may contribute to the spread of dengue in southern Europe. Longer stints of high temperatures offer more time for the mosquitoes to breed, ultimately resulting in more mosquitoes as summers start early and stretch late into fall.
Expansion of established mosquito populations
"The Aedes albopictus mosquito was first detected in Europe in the early 2000s," said Oliver Brady, a professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, who leads the Dengue Mapping and Modelling Group.
"It has since spread to many more areas around the Mediterranean and Central Europe and has increased in abundance in areas close to larger population centers," he told DW.
The mosquito population is currently established in all of Italy, Croatia, Bosnia, Albania, Slovenia, Hungary and in the majority of France. Since 2017, it has been established in Switzerland, parts of southern Germany and Austria.
However, unlike other types of mosquitoes, the Aedes doesn't venture far from its breeding area over its lifetime — only around 100 meters — which means it may take longer for it to spread to other areas, said Marianne Comparet, director of The International Society for Neglected Tropical Diseases.
This may help explain why we are just now seeing a heightened number of cases, Comparet told DW.
More travel-related transmission of the virus
Increased spread of dengue in Europe also depends on the increased spread of dengue in countries where the virus is endemic. The more dengue in a place, the more likely travelers will become infected and bring it home.
"Dengue cases outside of Europe have doubled between 2010 and 2022, meaning we are now much more likely to see introduction of the virus," said Brady.
Cases reported to the WHO increased from around 500,000 cases globally in 2000 to 5.2 million in 2019. So far, cases reported in 2023 total over 4.5 million.
But the WHO says cases are under-reported and estimates the actual number per year is probably closer to nearly 400 million worldwide.
Vector control and awareness
Vector control describes measures used to limit or eradicate human contact with the "vector" — the thing that transmits a disease — the mosquito.
Research suggests that European communities do not know how to respond to emerging public health threats.
For example, Comparet cited an example where health officials in Paris fumigated the home of a person who had arrived back home with dengue in August 2023. It was the first time insecticide had been used in this fashion in the French capital to fight the spread of the virus. But it may have been an unsuitable response, said Comparet, because the fumigation was done at night — but the Aedes species is most active during the day.
Comparet said doctors across Europe should increase their awareness of the symptoms of dengue, because most cases are mild or asymptomatic and therefore hard to spot if you don't know what to watch out for.
That said, Jaenisch admitted we don't even know how the threat will develop over the summers — and warm springs and autumns — to come.
"Honestly, we could be witnessing a stochastic event that will not repeat itself in the next 2-3 years and then again materialize," said Jaenisch.
Even if no one knows for sure, it pays to be aware.
Edited by: Zulfikar Abbany
(The above story first appeared on LatestLY on Nov 28, 2023 11:00 PM IST. For more news and updates on politics, world, sports, entertainment and lifestyle, log on to our website latestly.com).













 Quickly
Quickly