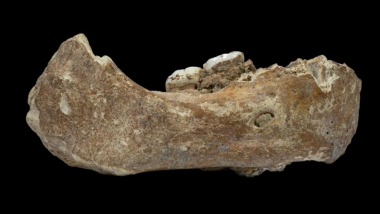
Amid speculations about supposedly Yeti footprints that were recently found in Nepal's base camp by the Indian Army, another mysterious object, a big human jaw has revealed more about human evolution. The Indian Army shared few pictures of mysterious footprints and claimed it to be of Yeti, the mythical creature. The mention of Yeti caused a buzz all over. This jaw with two huge teeth was found in the confines of a cave in 1980, a detailed analysis of it was revealed just a day ago. The human jaw was not as similar to what we have evolved into today. A Buddhist monk had entered a cave in Tibet to pray when he found it. And a detailed analysis of this was published in the scientific journal Nature. Is Yeti Real? Indian Army Shares Pictures of Yeti's Footprints Found in Himalayas; Know About the Folklore Beasts.
The study reveals that the ancient jaw belongs to the early human population called Denisovans- a sister group to the Neanderthals. The jaw dates back to 160,000 years ago. These results were based on a detailed analysis of the fossil as well as the proteins that were extracted from this bone. This jawbone is known as Xiahe mandible. This discovery gives a little more idea into ancient civilization development. Is Yeti Real or Not? 'Himalayan Mythical Beast' Footprints Shared by Army Most Likely Belong to Bear, Says Science Experts.
View Pics of the First Human Denisovan Jaw Found in Tibet:
1st fossil jaw of the Denisovans finally starts to put a face on our enigmatic human relatives. Biggest Denisovan fossil yet was found on the Tibetan Plateau, showing they were widespread--and lived at altitude. (Nat) https://t.co/tHTAdL9upi pic.twitter.com/atjxJaeY2E
— Steven Ashley (@steveashleyplus) May 1, 2019
This is not the first finding of a Denisovan fragment. But other findings have been made from the Denisova cave in Siberia. Today people all across Asia carry Denisovan DNA in their genomes. Since this particular jaw was found about 1,400 miles away from the Siberian cave, it highlights how the Denisovans ventured far into the other continent. This finding also suggests how the Denisovans evolved genetically to adapt to the higher altitudes. Many people from the Sherpa and Tibetan communities have inherited those genes after the interbreeding between Denisovans and modern humans in prehistoric times. 560,000-Year-Old Tooth Discovered by a Teen Archaeologist in a French Cave.
While the jaw was found in 1980s the research on it only began three decades later. The team took a lot of time to discover piece by piece information tracing from its finding to the ancient past.
(The above story first appeared on LatestLY on May 02, 2019 01:34 PM IST. For more news and updates on politics, world, sports, entertainment and lifestyle, log on to our website latestly.com).













 Quickly
Quickly