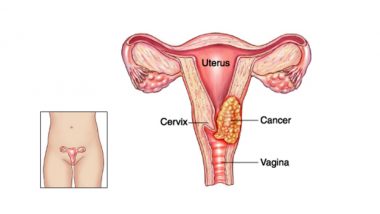
The lower part of the womb or the Uterus is called the ‘cervix’, and cancer affecting this part is known as ‘Cervical Cancer’. As per the GLOBOCAN 2018 statistics, Cervical Cancer is the 2nd most common Cancer among Indian women. Almost 1,00,000 new cases of Cervical Cancer are detected in India every year! In observance of World Cancer Day on 4th February, which is themed ‘I Am and I Will’, aims at spreading awareness about different types of cancers, so millions of deaths can be prevented, and treatment can be sought on time. World Cancer Day 2019: Cancer Cure to Become a Reality by the End of This Year? MAJOR Medical Breakthrough Offers Hope to Cancer Survivors.
According to WHO reports, Cervical Cancer is caused by sexually acquired infection, with certain types of Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). HPV is the most common viral infection of the reproductive tract. Most sexually active women and men will be infected at some point in their lives, and some may be repeatedly infected. HPV is sexually transmitted, but penetrative sex is not required for transmission; genital contact is a well-recognised mode of transmission. The risk of HPV exposure and thereby the risk of Cervical Cancer increases when one has multiple sexual partners and especially women with a history of sexually transmitted diseases, as well as smoking. Women with low immunity such as those on Immunosuppressive Therapy including steroids, women with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection or those in the post-transplant category, are also at an increased risk for Cervical Cancer.
Dr Uma Dangi, Consultant-Medical Oncology, Fortis Hospital, Mulund, shares with us symptoms of cervical cancer include:
- Abnormal vaginal spotting or bleeding or discharge
- Bleeding from the vagina in women who have achieved menopause requires urgent evaluation to rule out Cervical or Endometrial Cancer
- Lower abdominal pain or pain and bleeding after sexual intercourse
- In the presence of these symptoms, one must consult a doctor and get thoroughly evaluated to rule out Cervical Cancer.
Dr Uma Dangi also speaks about the Importance of PAP smear Screening, she says. Fortunately, this is the easiest gynaecological Cancer to be prevented through screening and early vaccination. Screening is done using a test called ‘Pap smear’. In this test, cells are collected from the cervix and examined under the microscope for the presence of any abnormalities. Before Cervical Cancer develops, there are options to treat these abnormal cells. PAP smear is recommended for all sexually active women over the age of 30yrs, every three years, till the age of 65yrs, depending on the results.
Additionally, one can reduce the risk of Cervical Cancer by adopting safe sex practices, such as the use of condoms and timely treatment of infections of the reproductive tract. Vaccines targeting HPV are also currently available. However, these are not effective against all HPV types that cause Cancer; and vaccination is not a replacement for screening. Women who have not been exposed to the HPV infection are likely to benefit more from the vaccine. Vaccination is given to girls between the ages of 9-14yrs; all parents with girls in this age group must speak to their doctor about HPV vaccine for their child.
It is essential to be aware of one’s risk of Cancer and get screened for early detection, which helps protect you and prevent the Cancer from developing.
(The above story first appeared on LatestLY on Feb 04, 2019 01:12 PM IST. For more news and updates on politics, world, sports, entertainment and lifestyle, log on to our website latestly.com).













 Quickly
Quickly