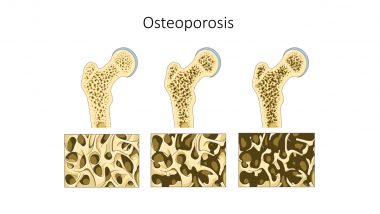
Researchers have succeeded in compiling an atlas of genetic factors associated with estimated bone mineral density (BMD), one of the most clinically relevant factors in diagnosing osteoporosis. The research, published in the journal Nature Genetics, identified 518 genome-wide loci, of which 301 are newly discovered, that explain 20 per cent of the genetic variance associated with osteoporosis.
Having identified so many genetic factors offers great promise for the development of novel targeted therapeutics to treat the disease and reduce the risk of fracture. "Our findings represent significant progress in highlighting drug development opportunities," said Brent Richards, a geneticist at the Jewish General Hospital (JGH) in Canada. Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Options and Why This Bone Disease Affects Men and Women Differently.
"This set of genetic changes that influence BMD provides drug targets that are likely to be helpful for osteoporotic fracture prevention," said Richards.
Osteoporosis is a very common age-related condition characterised by the progressive reduction of bone strength, which results in a high risk of fracture. Especially among older patients, fractures can have severe consequences, including the risk of mortality.
Among all sufferers, fractures impose major burdens of hospitalisation and extended rehabilitation.
As the population ages, the urgency of improving preventive measures becomes all the more intense. "We currently have few treatment options, and many patients who are at high risk of fractures do not take current medications because of fear of side effects," said Richards.
"We can prescribe injectables that build bone, but they are prohibitively expensive. We have medications that prevent loss of bone, but they must be taken on a strict schedule," he said. "As a result, the number of people who should be treated, but are not, is high. Therefore, we believe that we will have greater success in getting patients to follow a treatment regimen when it can be simplified," said Richards.
This was the largest study ever undertaken of the genetic determinants of osteoporosis, assessing more than 426,000 individuals in the UK Biobank. After analysing the data, the researchers further refined their findings to isolate a set of genes that are very strongly enriched for known drug targets.
This smaller set of target genes will allow drug developers to narrow their search for a solution to the clinical problem of preventing fractures in those people who are predisposed to osteoporotic fractures. Animal models have already proven the validity of some of these genes.
"Although we found many genetic factors associated with BMD, the kind of precision medicine that genetics offers should allow us to hone in on those factors that can have the greatest effect on improving bone density and lessening the risk of fracture," said John Morris from McGill University in Canada.













 Quickly
Quickly